All of us have, at least once a day, gone nearly blind due to bright Glare coming from the ground, windows, car bumper, snow, etc. And sometimes, we are crossing a road, riding a bike, or at some critical point where eyesight is most needed, and this blinding Glare causes us a lot of trouble. Do not worry; this Glare can be avoided by wearing Polarized Lenses Sunglasses.
If you are a Polarized glasses user or just a curious person wanting to know if they work, how they work, and how they are even made, then you have come to the right place. In this reading, we will break down the whole sci-fi advanced stuff in short easy steps.
So, keep reading if you are committed to the wonders of science, just like me.
Checklist
✓ What are Polarized Lenses?
✓ 3-Steps to make Polarized Lenses?
✓ What’s Next
1) What are Polarized Lenses?
“Lenses that cancel out the Glare are called Polarized Lenses. ”
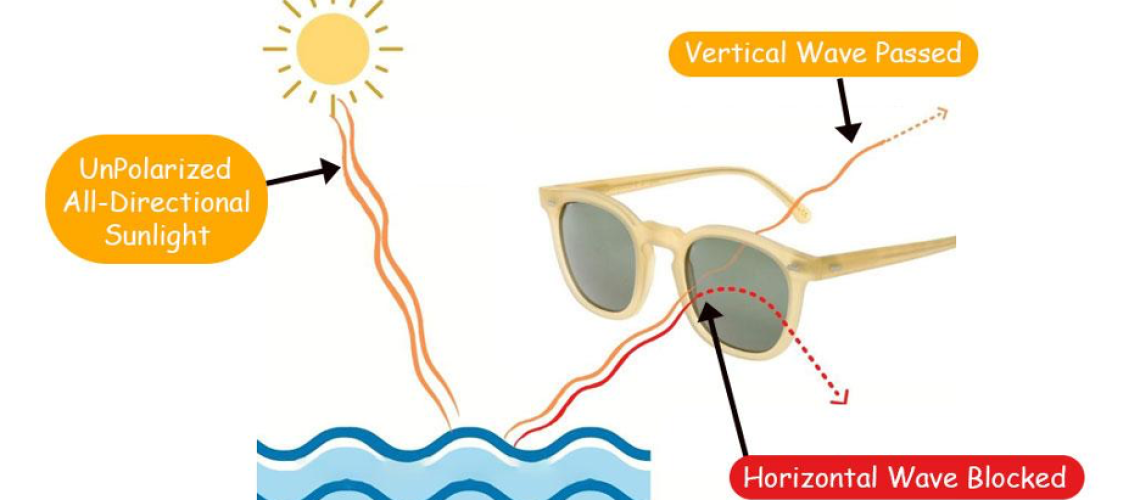
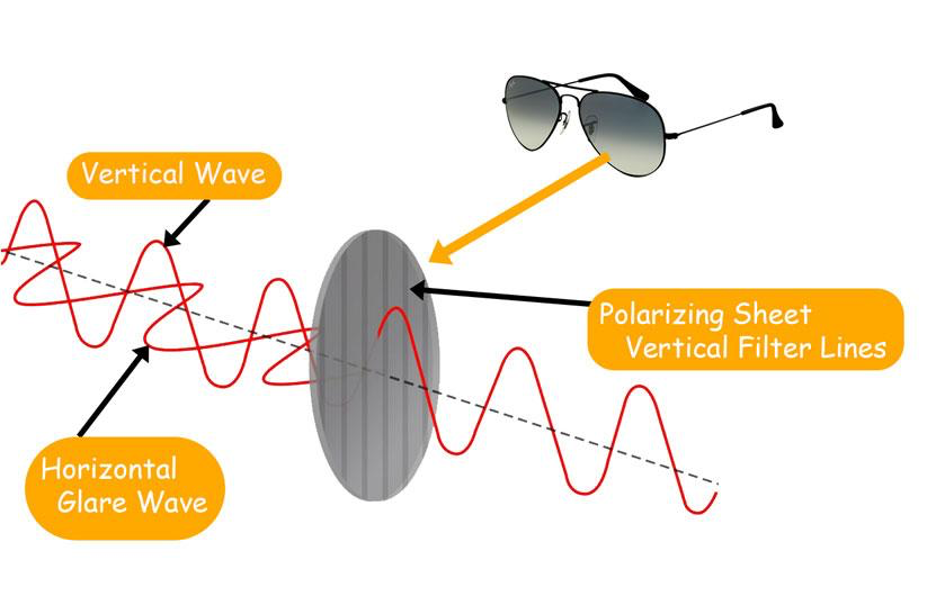
Polarized lenses work very simply; A light wave coming from the sun is evenly distributed among all angles, for example, vertical, horizontal, & every angle in between them.
But when Sunlight hits horizontal surfaces, like water, ground, snow, or your car bumper, most waves become polarized at one angle, “Horizontal”, also called Polarized Light. These concentrated horizontal light waves are very bright and cause a visual loss of varying degrees when they hit the eyes. This is what we call Glare.
We can stop the glare by eliminating Horizontal Waves, which we can do by adding unique Chemical Film, “Polarizing Sheets,” to normal lenses. This Polarizing Sheet has many vertical or horizontal lines; when horizontal light hits it, it gets blocked, and so does the glare. It allows vertical light waves to pass and produce a nice vision.
2) 3-Steps to make Polarized Lenses?
Lenses are tiny, like 4 mm ( less than half of a centimeter ), and the Polarizing sheet in them is microscopic, only 0.5 mm in thickness. So, manufacturing Polarized Lenses is very precise work that can only be done by advanced equipment & professional workers.
Here we will break down the Complex, multi-stage production of Lenses in just 3 Easy Steps, which are;
- Step no 1: Polarizing Sheet Production
- Step no 2: Plastic Film Bonding with Polarizing Sheet
- Step no 3: Lens fusing with Plastic Film
Step no 1: Polarizing Sheet Making
In this step, a 2.0 mm or less Polarizing Sheet is made. This Polarizing Sheet must have a Light Transmission value of 40% or higher and a co-efficient of Polarization of 99% or higher.
- First, a very thin Polyvinyl Alcohol ( PVA ) film, called Base Polarizing Film, is heated and stretched.
- PVA film then passes through a bath of Dychromatic Stuff, mostly Iodine. These Iodine crystals attach to Polyvinyl Alcohol ( PVA ) film in one Vertical or horizontal fashion and form equally placed vertical or horizontal lines filter all over the film, which will block horizontal waves.
- Then using an adhesive, a highly optically transparent layer of Cellulose triacetate is attached to the PVA film. That’s it; Our Polarizing Sheet is produced and ready to use in Lenses.
It is interesting to note that an adhesive used in this whole process must be highly transparent and have;
- Excellent stretchability during pressing
- High Heat resistance against molten lens material heat & hot process,
- Have other superior properties so that the high transparency is not affected in any way during the whole process.
Step no 2: Plastic Film Bonding with Polarizing Sheet
The only way to attach a Lens to a Polarizing Sheet efficiently is by pouring molten lens material on it and letting it fuse with the Polarizing Sheet. But, the Polarizing sheet is too weak to bear all the heat & shear pressure, and it will get destroyed instantly.
So, to overcome this problem, a layer of Plastic Film is introduced between the Lens & Polarizing sheet, which is done by;
- An adhesive film is attached to the Polarizing
- The Plastic Film of 0.1 ~ 0.5 mm thickness and 80% or higher light transmit ability is taken and fixed on the Polarizing Sheet Adhesive.
- This Polarizing Sheet & Plastic Film is placed in a Concave & Convex shape hot-press machine. And hot-pressed for 2 minutes to form a lens shape-polarizing sheet.
It must be noted that the thickness of Plastic film cannot be lower than 0.1 mm; otherwise, molten lens material will break it and reach the polarizing Sheet.
Plastic Film can not be higher than 5.0 mm because it is too thick to fuse, and under hot-press in too quick heat is applied, molecular stress will be produced, which will cause degradation in its optical qualities. This problem can be solved by using slow heat, but this will not be economical for mass-production factories.
Plastic film is mostly made of a Resin material which is fusible & compatible with the lens material. For example, the most used Plastic Film resin materials are;
- Polyester
- Polyether
- Polyacryl
- Polycarbonate
- Polyamide,
- Cellulose
- Polyurethane,
- Any of the above can be used singularly or in mixed form.
Step no 3: Lens fusing with Plastic Film
Now, its time to fuse the Lens with the Polarizing Sheet & Plastic Film we produced earlier, which is done;
- A Lens Material is taken, heated at high temperatures ( 150° C, 240° C, etc. ), and melted into a molten form.
- If a manufacturer wants to tint, various chemical mixtures are added in different amounts to control the intensity and frequency of light passing. This step also gives the lenses their particular tinted color, Blue, Brown, Dark, Purple, Green, etc. Some producers also did tinting afterward lens formation using the dying or spray method.
- The Polarizing Sheet is placed in a Molding cavity ( with convex & concave shapes ), and molten lens material is injected into it. The plastic film melts and fuses with the Lens resin in a unitary form, which will have superior optical properties.
And that’s it; Our Polarized Lens is formed. Some manufacturers add a lens on one side, and the other side of the Polarizing sheet is naked, which can be scratched easily. Premium High-quality Sunglasses have a Polarizing sheet sandwich between two lenses. Afterward, it goes to cutting, grinding, focal finding, harmful UV rays protective coating, and other machines for further processing according to its usage.
The most famous material to make lenses is;
- i) Glass ( superior optical quality but bulky, easily breakable, and costly )
- ii) Various Resins ( Superior Impact Resistance, Cost-effective, Lightweight )
The Resin materials which can be used to make lenses are polycarbonate, polyacrylate, polyamide, cellulose, polyester, polyester-urethane, polyether-urethane, etc.
➢ What’s Next
I hope you fully understand how polarized lenses work & made and why you should prefer them over non-polarized sunglasses.
But, they also have some demerits, like all liquid crystal display devices will be seen dim, like your computer screen, mobile display, etc. And some other demerits, which we will discuss another time.
However, the main point is that polarized sunglasses work and stop dangerous blinding glare; without them, you may end up in a terrible accident.